
Copy these to the folder '/var/lib/tftpboot'. There are three files you need here: 'menu.c32', 'ldlinux.c32' and 'libutil.c32'. The 'c32' files are modules that run in SYSLinux, which we will use the file 'menu.c32'.įor Ubuntu, the files are in '/usr/lib/syslinux/modules/bios'. There are files located here with the extension 'c32'. The system stores the SYSLinux files under the folder '/usr/share/syslinux/'. The command installs the TFTP client (tftp), the TFTP Server (tftp-server) and SYSLinux (syslinux) to your server.
TFTP CLIENT DOES NOT ACCEPT OPTIONS INSTALL
Sudo apt install tftp tftp-server syslinux -y Sudo yum install tftp tftp-server syslinux -y The command to install TFTP and SYSLinux is:
Next, it is necessary to install the TFTP services to Server1 along with the SYSLinux files. In our case, we are using the PXELinux to allow our clients to network boot. PXELinux – booting from a network device.EXTLinux – boot from a drive formatted as EXT or BRTFS.SYSLinux is a very simplified Bootloader, not as complex as 'GRand Unified Bootloader' (GRUB). Our first step is to install a TFTP client and server. So, we need to change our Server1 system to handle PXE booting clients. NOTE: Otherwise noted, the commands work for CentOS and Ubuntu. To make this work, we need to add the TFTP Service and change the DHCP Configuration. We have previously set up a DHCP Service on Server1 and an FTP Service. We previously set up a client in VirtualBox to perform the PXE booting function from our Server1 machine in VirtualBox. The menu will allow the user to perform an automated install or boot from the local disk, the default option.
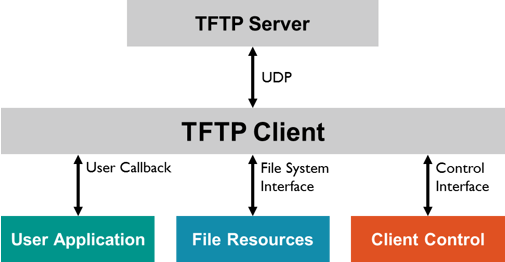
In our case, the file downloaded to the client will be a menu. Configurations from the DHCP Server will cause the PXE client to contact another server for instructions, in this case a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Server. Once booted, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server gives an IP Address to it.

The Preboot Execution Environment (PXE), commonly referred to as 'pixie', is a means to boot from a Network Interface Card (NIC) to the network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
